How Black clergy are reframing approach on abortion with congregations

[ad_1]
(RNS) — For the Rev. Irene Prince, discussions around reproductive choice start in Bible study.
Prince, pastor of Mount Olive AME Church in Emporia, Kansas, has taught on the biblical concept of free will in connection with choice — a connection she hopes will move her congregation to “demonstrate the love of God” by being kinder and not passing judgment on how people decide to live their lives.
“We don’t have to be the keepers of behavior and the purveyors of what is supposed to be holy. That’s God’s realm. I have no heaven or hell to put anybody in,” said Prince, who is also trying to address reproductive issues by inviting health professionals and advocates to speak to her predominantly Black congregation.
While white evangelicals have led anti-abortion movements and publicly celebrated the U.S. Supreme Court’s decision overturning Roe v. Wade last June, responses from within the Black church have been more mixed and muted. A recent Pew Research survey found that two-thirds of Black Protestants (66%) believe abortion should be legal or mostly legal in all cases — a sharp contrast to the 74% of white evangelicals who believe it should be illegal or mostly illegal in all cases.
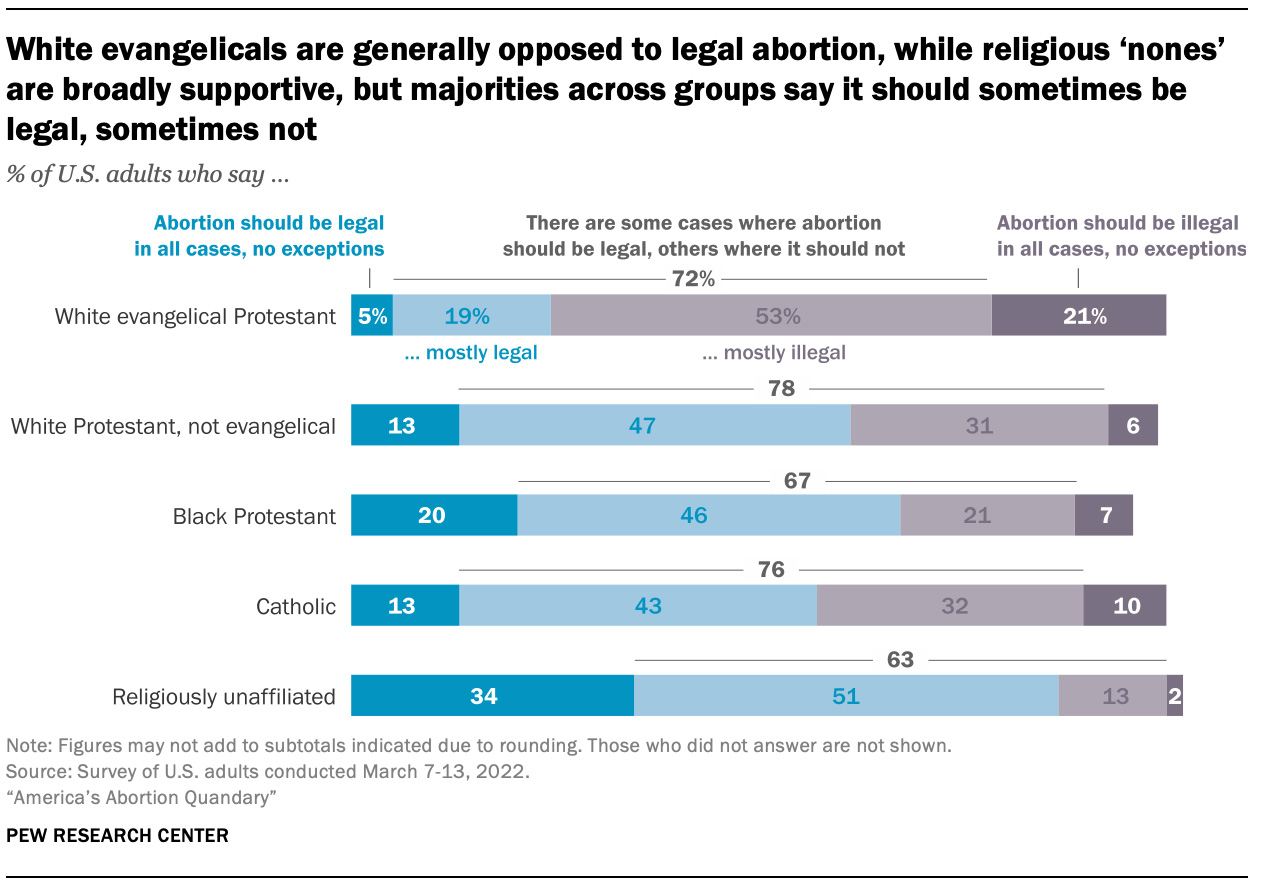
“White evangelicals are generally opposed to legal abortion, while religious ‘nones’ are broadly supportive, but majorities across groups say it should sometimes be legal, sometimes not” Graphic courtesy of Pew Research Center
Even as some of the largest Black denominations oppose abortion and Black clergy often hold theological positions affirming the sanctity of unborn life, they also face the reality that Black women, who make up the majority of their congregations, are disproportionately affected by lack of access to reproductive health services.
“Nobody flippantly makes that decision,” said Prince. “We forget that people have choices in their life that they have to make. Those choices are difficult enough without us interfering in their life in a way that is harmful, that ignores their humanity.”
Not all clergy feel theologically equipped to broach the topic of reproductive health, said the Rev. Madison Shockley, former member of the Planned Parenthood Clergy Advocacy Board and pastor at Pilgrim United Church of Christ in Carlsbad, California.

The Rev. Madison Shockley. Courtesy photo
In his advocacy work and in his ministry, he tries to help clergy take “the Bible seriously, not literally,” by using the Jewish cultural context of the Bible as an entry point to discussing reproductive health from the pulpit.
“Jewish theology has always held — and Christian theology adopted this for many centuries — that life begins with the first breath of the fetus, not conception,” he said.
Monique Moultrie, associate professor of Africana studies and religious studies at Georgia State University, said more pastors are taking a “whole life” approach to reproductive access in church settings instead of engaging in politically charged, single-issue debates around the morality of abortion.
Some ministers are operating in “triage mode” to help church members with funds or day care services when they need to travel across state lines for abortion access, said Moultrie, who sees these offerings as an entry point for ministry leaders to expand their ministries to women and children.
Clergy are “thinking through these things in ways that I think will transform how we think of the Black church’s impact because there really is this gap between the baby and youth ministry,” she said. “Our responsibility doesn’t just start and end with the baby dedication.”
Cherisse Scott sees an awakening happening among Black clergy to address reproductive justice. That’s a positive sign, said Scott, founder and CEO of the Memphis-based reproductive advocacy nonprofit SisterReach. She recognizes clergy play a critical role in their communities.

Cherisse Scott. Courtesy photo
“We are interested in equipping them with the ability to be spokespersons for this work,” said Scott.
SisterReach offers clergy a range of reproductive justice resources, from consultation services, to tips on talking with members about abortion access, to strategies for lobbying legislators on behalf of their communities. SisterReach also created the Interfaith Coalition for Human Rights, composed of clergy around the country who do “movement evangelism,” advocating for reproductive justice and sexual health care, among other issues.
“Approaching this as an abortion conversation is what got us here,” said Scott, who is also an ordained minister. “Approaching this as a conversation around abundance is what will get us out of this.”
Brandee Jasmine Mimitzraiem, director of institutional engagement and public theology with the Religious Coalition for Reproductive Choice, said the people in the pews are often less hesitant to start conversations around reproductive justice than their pastors. Only 22% of Black churchgoers heard sermons about abortions, compared with 31% who heard sermons on criminal justice reform, according to a 2021 Pew Research Center study.
As a former pastor, Mimitzraiem has seen her members respond positively to partnering with reproductive justice organizations, recognizing they have a desire to understand the injustice around abortion access rather than an opportunity to gossip about each other’s sexual behaviors. She believes this is the time for congregations to make their voices heard.
“Congregations have a whole lot more power than they think they do,” Mimitzraiem said. “People want to know how to do this justly from a faith lens, from a lens that’s rooted in the Black church.”
[ad_2]
Source link
