After Years of U.S. Military Aid, Terror Attacks Still Rise in Niger

[ad_1]
NIAMEY, Niger — The look on Miriam’s face was abject fear. Her pink, white, and green veil had mostly slipped from her head, and her dark eyes grew wide as she stared down at her lavender smartphone. In a flash, she pulled it to her ear. “Allo!” she said, her pitch rising as her other hand nervously cradled her chin.
In the courtyard of her family’s tree-lined compound in a well-to-do neighborhood in Niger’s capital, members of Miriam’s ethnic group had been describing jihadist attacks on their historic community in a rural region to the north. Now, the six or seven men wearing tagelmusts — a combination of turban and scarf worn by Tuareg men to provide protection from sun and dust — were also glued to their phones as chimes announced incoming texts and calls. Voices on the phones sounded panicked. There were gunshots, and a familiar roar rumbled through the desert scrubland 100 miles away. At any moment, relatives warned, they expected an attack by the “motorcycle guys.”
Over the last decade, Niger and its neighbors in the West African Sahel have been plagued by terrorist groups that have taken the notion of the outlaw motorcycle gang to its most lethal apogee. Under the black banners of jihadist militancy, men on “motos” — two to a bike, their faces obscured by sunglasses and turbans, armed with Kalashnikovs — have terrorized villages across the borderlands where Burkina Faso, Mali, and Niger meet. These militants, some affiliated with Al Qaeda or the Islamic State group, impose zakat, an Islamic tax; steal animals; and terrorize, assault, and kill civilians.
Jihadist motorcyclists, Miriam reminded me, had thundered into the village of Bakorat on March 21, 2021. As described afterward by one of the survivors, the motos “swept into the village like a sandstorm, killing every man they saw. They shot one of my uncles in front of me. His 20-year-old son ran to save him, but he perished as well. We found them, slumped over each other.” Attacking in overwhelming numbers and with military precision, the jihadists executed men and boys while looting and burning homes. “They attacked the well like it was a military objective, opening fire on the dozens of men there. As they killed, I heard the attackers saying, ‘This is your time … for working with the state,’” another survivor told Human Rights Watch. “I collapsed, seeing the carnage … my father, my brothers, my cousins, my friends lying there, dead and dying.” Human Rights Watch said more than 170 people were massacred near Bakorat and Intazayene villages and nearby nomad camps that day. Miriam and her relatives put the number at 245.
As we sat in the courtyard, it all seemed to be happening again.

Photo: Carley Petesch/AP
In fact, Niger hosts one of the largest and most expensive drone bases run by the U.S. military. Built in the northern city of Agadez at a price tag of more than $110 million and maintained to the tune of $20 to $30 million each year, Air Base 201 is a surveillance hub and the lynchpin of an archipelago of U.S. outposts in West Africa. Home to Space Force personnel, a Joint Special Operations Air Detachment, and a fleet of drones — including armed MQ-9 Reapers — the base is an exemplar of failed U.S. military efforts in this country and the wider region. With terrorism skyrocketing in the Sahel while the U.S. pours hundreds of millions of dollars into security assistance, base construction, and troop deployments, this drone outpost — built to enhance security in the region — can’t even protect its own contractors and the U.S. tax dollars that keep it running. Less than a mile from the base’s entrance, as The Intercept recently reported, bandits conducted a daylight armed robbery of base contractors and drove off with roughly 24 million West African CFA francs late last year.
U.S. troops in the country also train, advise, and assist local counterparts and have fought and even died — in an ambush by ISIS near the village of Tongo Tongo in 2017. Over the last decade, the number of U.S. military personnel deployed to Niger has jumped more than 900 percent from 100 to 1,001. Niger has seen a proliferation of U.S. outposts that includes not just the huge drone base in Agadez, but also another one in the capital, at the main commercial airport. You can sit in a departure lounge and watch drones land and take off.
Last month, U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken met with Niger’s President Mohamed Bazoum and decried the growing regional influence of the Russian mercenary Wagner Group. “Where Wagner has been present, bad things have inevitably followed,” said Blinken, noting that the group’s presence is associated with “overall worsening security.” The U.S. was a better option, he said, and needed to prove “that we can actually deliver results.” But the U.S already has a two-decade record of counterterrorism engagement in the region — and “bad things” and “overall worsening security” have been the hallmarks of those years.
Throughout all of Africa, the State Department counted a total of just nine terrorist attacks in 2002 and 2003, the first years of U.S. counterterrorism assistance to Niger. Last year, the number of violent events in Burkina Faso, Mali, and western Niger alone, reached 2,737, according to a new report by the Africa Center for Strategic Studies, a Defense Department research institution. This represents a jump of more than 30,000 percent since the U.S. began its counterterrorism efforts. (Wagner has only been active in the region since late 2021.) During 2002 and 2003, terrorists caused 23 casualties in Africa. In 2022, terrorist attacks in just those three Sahelian nations killed almost 7,900 people. “The Sahel now accounts for 40 percent of all violent activity by militant Islamist groups in Africa, more than any other region in Africa,” according to the Pentagon’s Africa Center.
The impact of armed conflict and forced displacement on Nigeriens has been enormous.
Last year, an estimated 4.4 million people experienced dire food insecurity — a record number and a 90 percent increase compared to 2021. Between last January and September, almost 580,000 children under 5 suffered from wasting. This year, the United Nations estimates that about 3.7 million Nigeriens, including 2 million children, will need humanitarian assistance. Many of those in need are also the most difficult to reach due to insecurity.
It’s worth noting that in 2002, when the U.S. began pumping counterterrorism funds into the country, the overall food situation was described as “satisfactory” and undergoing “progressive improvement,” according to a food security monitoring agency set up by the U.S. Agency for International Development.
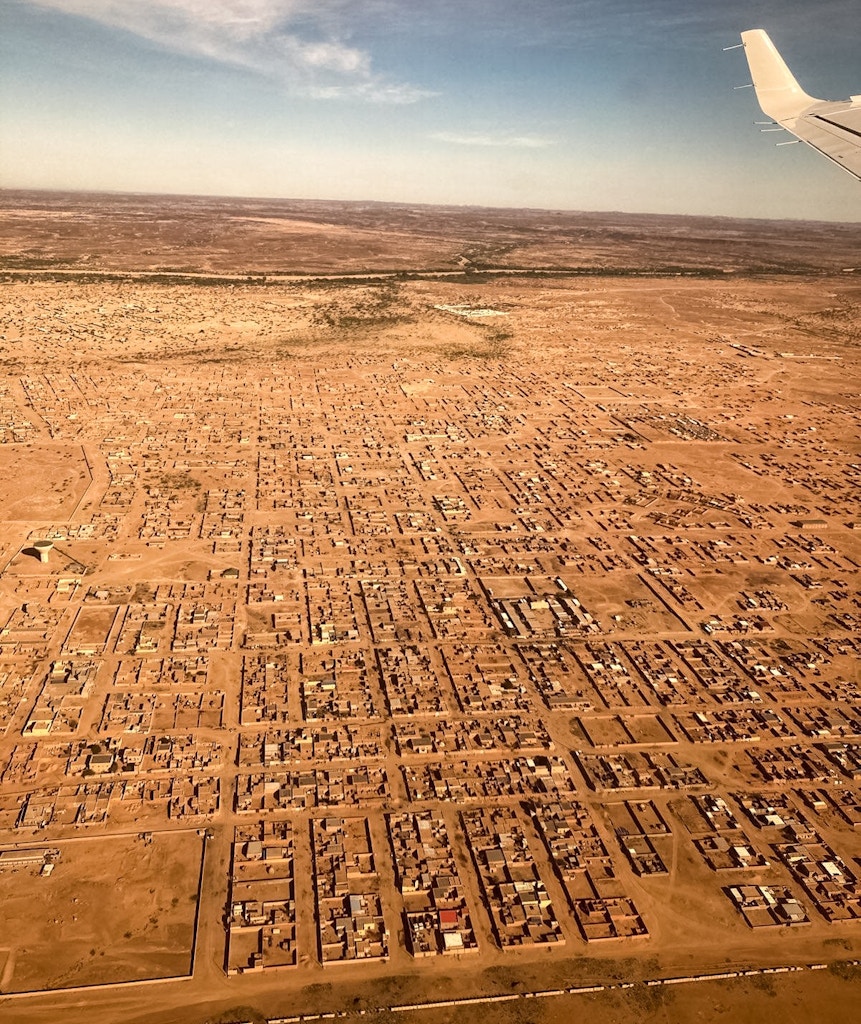

Agadez, Niger as seen from the air on January 13, 2023. This northern town is home to Air Base 201, a surveillance hub and the lynchpin of an archipelago of U.S. outposts in West Africa.
Photo: Nick Turse
Banning Motorbikes
As quickly as it began, the telephonic flurry of rings and chimes that took over Miriam’s courtyard in Niamey ceased. I heard later that one motorbike was spotted — and that the gunfire may have been shots from the local self-defense group at the rider of that moto.
To Miriam and her relatives, shooting at someone for riding a motorcycle sounds completely prudent. This mindset meshes with a parade of government policies instituted in the tri-border region and the far east of the country, near Lake Chad, where the terror group Boko Haram has been a persistent menace.
Niger and its neighbors have intermittently imposed emergency measures, including the banning of motorbikes. Local markets have also been closed because authorities say that terrorists use them to purchase supplies. There have been other restrictions on people’s movement, the purchase of fertilizer, and fishing — all in the name of counterterrorism. Violating these strictures may brand you as a terrorist or sympathizer. Your ethnicity may too. People in this compound, just like those in the Nigerien government, will tell you that while many jihadists are ethnic Peul, all Peul are not jihadists. They also say there is no ethnic component to this conflict. Peul leaders disagree. They say they’re the victims.
A week later, I’m in a different compound in another part of town to meet two men who want their stories told. As we sit in a darkened room, I ask if it’s OK to use their names; they shoot each other worried looks. “The military will come find us. They’ll say, ‘You talked to the journalist,’” said a man in a white tagelmust as his colleague in a blue turban nodded. It’s a common fear here. People are afraid of their U.S.-backed government, so while they gave me their names and those of their villages, I can only call these men “Puel community leaders.”
“The emergency measures just impoverished people. The jihadists kept their motos. They were able to purchase supplies. They eat and drink. They do whatever they want. But average people lost everything.”
“The emergency measures just impoverished people. The jihadists kept their motos. They were able to purchase supplies. They eat and drink. They do whatever they want. But average people lost everything,” the man in white explained. “There’s a 6 p.m. curfew, but it takes two days by moto to travel to the health clinic. People are dying because they can’t get treatment.” The man in blue explained that the closure of markets meant finding a car — another major expense — to drive to Mali. “So instead of paying 10,000 CFA for a sack of millet, you pay 50,000 CFA,” he said, referring to the local currency, West African CFA francs. “There’s a lot of hunger.”
Predominantly seminomadic Muslim cattle herders, ethnic Peuls across the Sahel express discontent with government neglect of their communities. Many say they have been tagged as terrorists, and the stigma has further marginalized them and encouraged abuse by government troops. “They arrest people without cause,” said the leader in white. “Peul youth laid down their arms and wanted to join the state security forces or form a militia, but the government rejected the offer.”
Hassane Boubacar, a colonel major — a rank between colonel and general — and an expert on radicalization detailed to the Nigerien prime minister’s office, agreed that socioeconomic issues are key drivers of terrorism. “The jihadists do what the state fails to do and provides services that the government fails to provide,” he said. “The people in these areas are very poor, and the jihadists have a lot of money to pay them from illegal activity, like drug trafficking.”
A recent U.N. Development Program report on terrorism in sub-Saharan Africa found much the same. Drawing on interviews with 2,200 people in Niger, Mali, Burkina Faso, and five other African nations, UNDP discovered that roughly 25 percent of voluntary recruits cited job opportunities as their primary reason for joining terror groups. Only 17 percent mentioned religion. The report found that most who joined extremist groups grew up “suffering from inter-generational socio-economic marginalization and underdevelopment.”
As a disaffected minority, the Peul have been the prime focus for recruitment by Islamist militants, even as Peuls are often victims of jihadist attacks. “They say, ‘The Peul are terrorists,’ but the terrorists terrorize us,” said the Peul community leader in the white tagelmust. “They steal our animals. They kill our family members.” At the same time, Peul are also a prime target of arrests, abuse, and attacks by Nigerien security forces.
Nearly half of those interviewed for the UNDP report said a specific event pushed them to join militant groups, with 71 percent citing human rights violations, often at the hands of state security forces. According to the report, “in most cases, state action, accompanied by a sharp escalation of human rights abuses, appears to be the prominent factor finally pushing individuals into [violent extremist] groups in Africa.”
Col. Maj. Boubacar was dismissive of reported Nigerien atrocities. “Sometimes, we’re accused of human rights violations,” he said. “But we pay a lot of attention to allegations.”
The U.S. government doesn’t agree. A State Department analysis of human rights in Niger released last month cited significant abuses, including credible reports of arbitrary and unlawful killings by the government. “For example, the armed forces were accused of summarily executing persons suspected of fighting with terrorist groups,” reads the report, which also details arbitrary detention, unjustified arrests of journalists, life-threatening prison conditions, and rampant impunity among the security forces.
In 2020, for example, Niger’s National Commission on Human Rights investigated allegations that 102 civilians had disappeared during a weeklong military operation. “There have indeed been executions of unarmed civilians and the mission discovered at least 71 bodies in six mass graves,” said Abdoulaye Seydou, the president of the Pan-African Network for Peace, Democracy, and Development, which took part in the investigation. “It is elements of the defense and security forces which are responsible for these summary and extrajudicial executions.” Witnesses told Human Rights Watch that an additional six mass graves containing 34 bodies were also uncovered nearby.
Last fall, the Nigerien military also bombed a gold mine during a counterterrorism operation. While the government claimed that only seven people died, locals said many more civilians were killed. After Seydou spoke out about it, he was charged with “publishing information likely to disturb public order” and arrested. The case was dropped, but as he attempted to leave the courthouse, Seydou was again arrested, cited for “creating false evidence to overwhelm” the Nigerien military and sent to a high-security prison.

Illustration: Michelle Urra for The Intercept
Direct Operations
As with allies the world over, from Cameroon to Saudi Arabia, human rights violations haven’t deterred the U.S. from supporting Niger’s government. Hang around the airport in Niamey and you’ll see a parade of white faces, tattooed arms, and goatees. Waiting for flights in and out of the country, you hear talk of the trials and tribulations of Veterans Affairs medical care. When discussing their seats on the plane, it isn’t 23D but 23-Delta. “What are you teaching?” a paunchy contractor with a Southern accent and a goatee asked a younger man with an artfully groomed beard traveling with a group of Americans who, it turned out, were providing instruction on battlefield medicine.
When asked what U.S. troops were doing in Niger, U.S. Africa Command spokesperson Kelly Cahalan offered a boilerplate response: “The U.S. military is in Niger at the request of the Government of Niger and we remain committed to helping our African partners to conduct missions or operations that support and further our mutual security goals and objectives in Africa.” What are those “missions or operations”? The most famous came to light in October 2017 when ISIS fighters ambushed American troops near Tongo Tongo, killing four U.S. soldiers and wounding two others.
AFRICOM told the world that a small group of U.S. troops were providing “advice and assistance” to local counterparts. In truth, the ambushed team was working out of the town of Ouallam with a larger Nigerien force under Operation Juniper Shield, a wide-ranging regional counterterrorism effort. Until bad weather prevented it, that group was slated to support another team of American and Nigerien commandos based in Arlit — a town 700 miles northeast of the capital — attempting to kill or capture an ISIS leader as part of Obsidian Nomad II, a so-called 127e program that allows U.S. forces to use local troops as proxies.
A 2018 investigation by then-Maj. Gen. Roger Cloutier found that AFRICOM’s advise-and-assist story was a fiction. “Missions described in this report and executed by Team OUALLAM and Team ARLIT were driven by U.S. intelligence, planned entirely by U.S. forces, and directed and led by [U.S. forces]. Nigerien forces had no input in the planning process or the decision to execute the missions,” he explained. “Advise, assist, and accompany operations that Team OUALLAM and Team ARLIT were conducting … more closely resembled U.S. direct action than foreign partner-led operations aided by U.S. advice and assistance.” Direct action, to be clear, is a special ops euphemism for strikes, raids, and other offensive missions.
Cloutier wrote that U.S. commandos in Niger “are planning, directing, and executing direct action operations rather than advising Nigerien-led operations.” Is this still the case? The official answer is no. But the official answer used to be that these were “advise-and-assist” missions. It took a tragedy that couldn’t be suppressed for the truth to slip out.
Commandos, however, don’t only conduct clandestine raids. When I happened to encounter three men who said their names were Cam, Chuck, and Brock at Agadez’s Ministry of Justice headquarters, they were on a different kind of mission. Cam sported a shiny lavender dashiki-style top — they call it bazin here — with an embroidered placket and matching lavender pants, dark wraparound sunglasses, a backward black baseball cap, and a beard that would satisfy the Taliban. He said he hailed from Colorado and had been in-country almost eight months. Chuck had more conventional facial hair, wore a green Fjallraven cap, a blue Osprey Daylite shoulder sling strapped tight to his chest with one radio or satphone carabineered to it and another walkie-talkie clipped to his pocket. Brock wore a black and gray ballcap, a polo shirt and khakis, a hand-held radio clipped to the right front pocket, and had a haversack strapped to his back.
While the U.S. spends significant time and money training, advising, and assisting Nigerien troops, Americans also devote substantial resources to courting government officials and building influence with local elites.
Cam said he was on a farewell tour and had a gift for the top local prosecutor. It highlighted another facet of American efforts in Niger — one that plays out across the globe whenever Americans sit down for an awkward cup of tea with, or provide Viagra to, some local chieftain they hope to win over. While the U.S. spends significant time and money training, advising, and assisting Nigerien troops, Americans also devote substantial resources to courting government officials and building influence with local elites.

Anastafidet Mahamane Elhadj Souleymane, a leading figure among the Association of Traditional Chiefs of Niger – representing more than 400 Tuareg villages – at his compound in Agadez, Niger on January 12, 2023.
Photo: Adoum Moussa
When I spoke with him recently, Mohamed’s tune had dramatically changed. He had gone from a vocal critic to an ardent believer. “In the beginning, they didn’t have anything to do with me,” he said of the U.S. military in Agadez. “Now, the Americans come here every two weeks, every month. They were here just yesterday. We exchange information about security issues,” he gushed. “I’m very pleased with the relationship.”
AFRICOM ignored questions about their relationship with Mohamed, but it seems clear that the U.S. military decided to court this formerly critical local leader. Mohamed showed me a certificate, commemorating a 2021 drone mission and bearing the logo of Special Operations Command Africa, presented to him by his American friends. But it didn’t stop with press-the-flesh attention and meaningless keepsakes. After Mohamed told the Americans about a nagging medical condition, he said that they brought him to the drone base in Agadez where he was treated by a U.S. doctor.
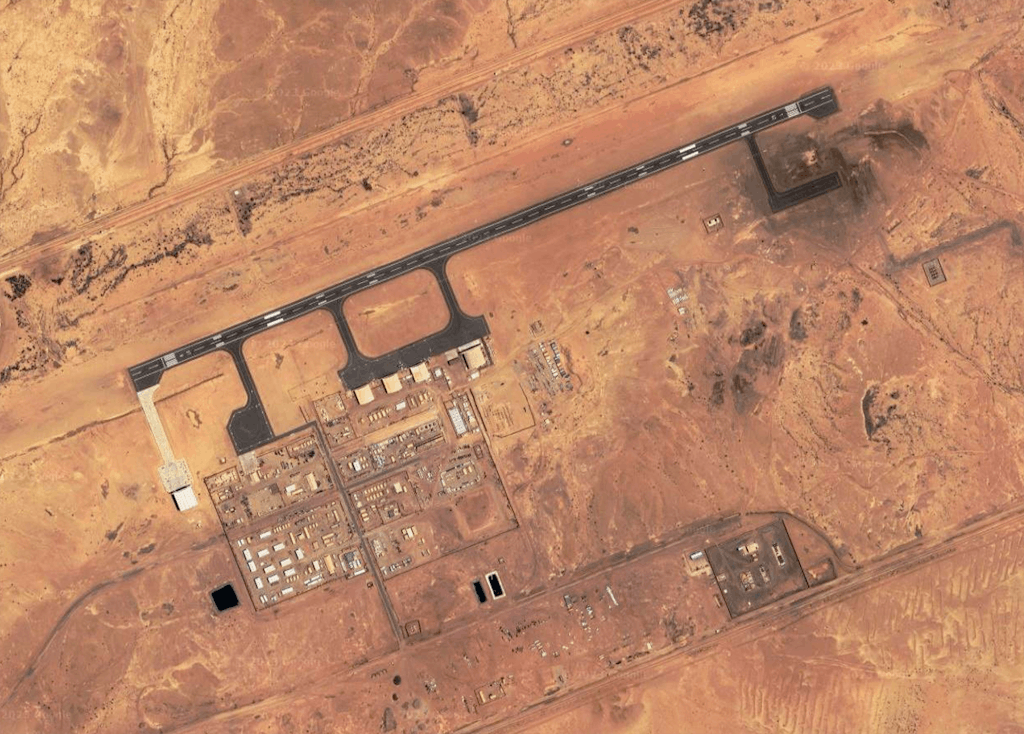
Air Base 201 in Agadez, Niger, 2023.
Photo: Google Maps
Drones and Hope
While the base may come up short as a surveillance and security bastion, it has had an undeniable impact. If you’re a local elite like Mohamed, the Americans apparently invite you in and provide you with free medical care. But if you’re living on the outskirts of the facility in the hard-scrabble Tadress neighborhood, it’s a different story.
To most in Tadress, Air Base 201 is a mystery. “We don’t know what they do there,” said several women in a rough-hewn compound a short distance from the outpost. The only tangible impact of the U.S. military on their lives, they told me, were the cracks that formed in their mud walls due to huge transport planes that shook their homes as they passed overhead.
Maria Laminou Garba, 27, runs a recycling collective in Tadress that pays unemployed youths to gather recyclables and subsidizes schooling for neighborhood orphans. When there were only Nigeriens at the base, Garba could make a little money selling them food. When the Americans arrived, she said she was no longer welcome. With permission from the mayor of Agadez to collect plastic in that section of Tadress, she approached the base with her young employees, hoping to gather discarded water bottles. But Garba quickly grew scared of the guards’ guns when a booming voice from a loudspeaker told them to leave.
The U.S. military touts good works in Tadress, like rebuilding a primary school. “I’ve heard about them helping, but I’ve never seen it,” said Garba. The U.S. also publicizes opportunities for locals to sell trinkets at craft bazaars at Air Base 201. “People from town get to sell stuff,” Garba told me, referring to Agadez proper. “They’re not from here.”
Garba and a local leader — the chef de quartier of Tadress, Abdullah Bil Rhite Chareyet — led me to a reservoir near the outskirts of the base where locals use the water to make mud bricks. But the site is also, they explained, a danger to children. “A 6-year-old child drowned here a few years ago,” said Garba. “Every year, someone dies here.” Last year, a 17-year-old girl became the latest victim, she and Chareyet told me.
Chareyet meets with American military personnel from time to time. They asked him to look out for suspicious activity — most notably sightings of Toyota Land Cruisers. (A Land Cruiser pickup truck apparently carried out the 2021 armed robbery on the outskirts of the base.) The Americans gave him a phone number to call in reports.
In 2021, after years of requests from the village chief for American assistance, Chareyet, Garba, and other local leaders met with a U.S. officer and his interpreter at this same spot. The American, they said, pledged to install a fence around the reservoir and post a guard, to protect local children. Chareyet showed me photos of him with the American. AFRICOM refused to comment on the man’s identity, but a U.S. contractor working at the base, who was not authorized to speak with the press, examined the images and verified that the man pictured was a civil affairs officer who had since left Niger.
Chareyet had hoped that the Americans would honor their word. But six months later, when I visited the site, there was no fence. Chareyet said the Americans had not been back. “I thought they would build the fence like they said,” he told me. Garba shook her head, adding, “The Americans gave us false hope.”
[ad_2]
Source link

